Hi, I'm Adrian! I am a PhD student in the Machine Learning Group at TU Berlin, where my research interests lie in automatic differentiation and explainable AI. I'm a huge fan of the Julia programming language and its community.
I like to spend my free time on open-source software, Go, good coffee and my bike. Some day I'm going to find the time to learn Rust.
Please reach out if you're interested in collaborating. Links to my Google Scholar and social media profiles can be found at the bottom of this page.
Smoothed Differentiation Efficiently Mitigates Shattered Gradients in Explanations
A. Hill, N. McKee, J. Maeß, S. Bluecher, K.-R. Müller
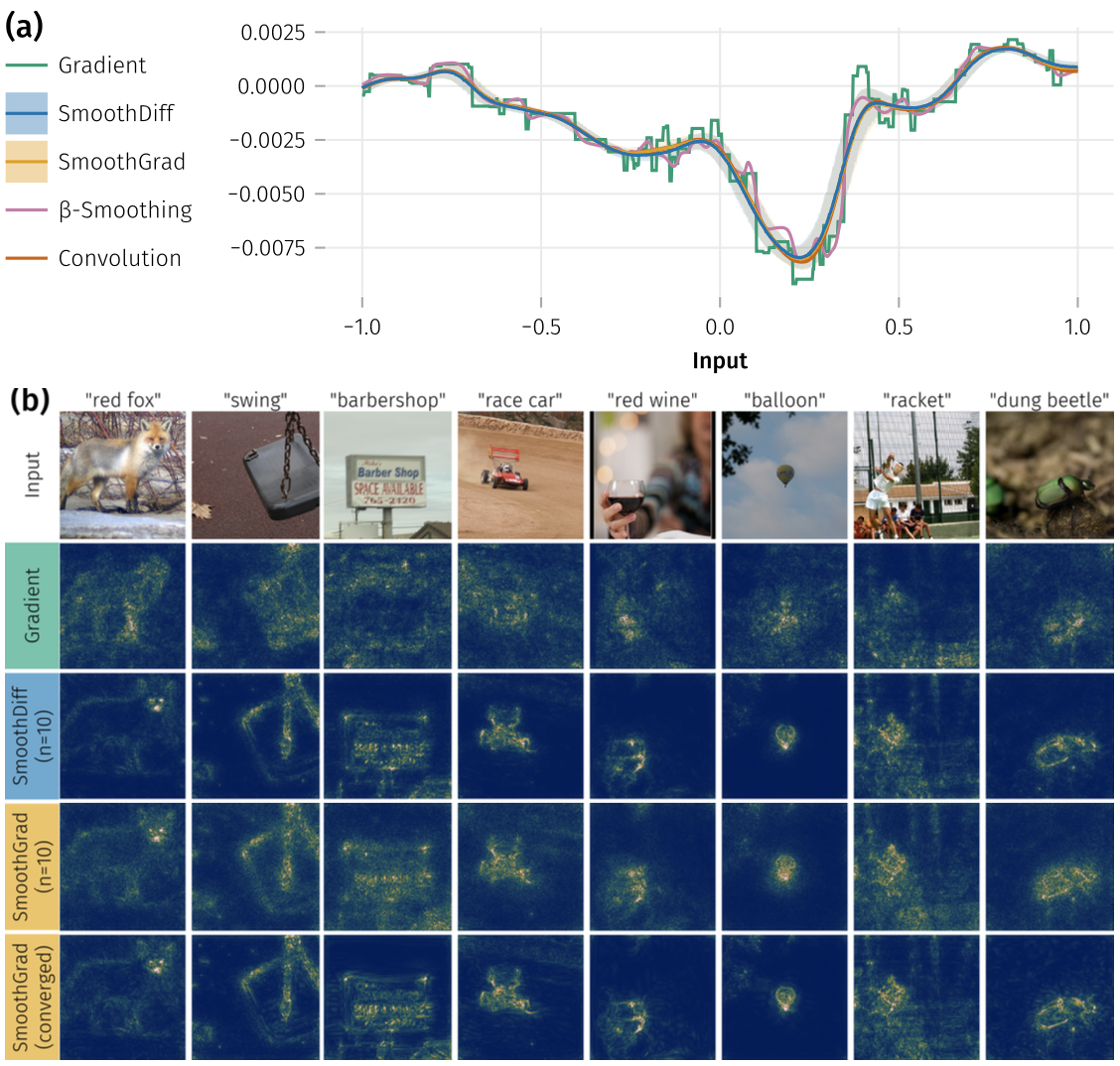
Explaining complex machine learning models is a fundamental challenge when developing safe and trustworthy deep learning applications. To date, a broad selection of explainable AI (XAI) algorithms exist. One popular choice is SmoothGrad, which has been conceived to alleviate the well-known shattered gradient problem by smoothing gradients through convolution. SmoothGrad proposes to solve this high-dimensional convolution integral by sampling — typically approximating the convolution with limited precision. Higher numbers of samples would amount to higher precision in approximating the convolution but also to higher computing demand, therefore in practice only few samples are used in SmoothGrad. In this work we propose a well founded novel method SmoothDiff to resolve this tradeoff yielding a speedup of over two orders of magnitude. Specifically, SmoothDiff leverages automatic differentiation to decompose the expected values of Jacobians across a network architecture, directly targeting only the non-linearities responsible for shattered gradients and making it easy to implement. We demonstrate SmoothDiff's excellent speed and performance in a number of experiments and benchmarks. Thus, SmoothDiff greatly enhances the usability (quality and speed) of SmoothGrad — a popular workhorse of XAI.
A Common Interface for Automatic Differentiation
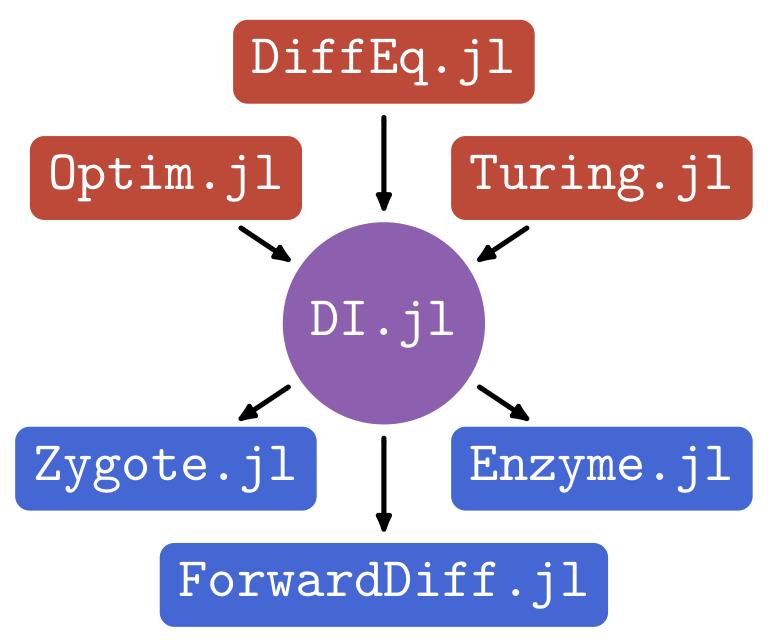
For scientific machine learning tasks with a lot of custom code, picking the right Automatic Differentiation (AD) system matters. Our Julia package DifferentiationInterface.jl provides a common frontend to a dozen AD backends, unlocking easy comparison and modular development. In particular, its built-in preparation mechanism leverages the strengths of each backend by amortizing one-time computations. This is key to enabling sophisticated features like sparsity handling without putting additional burdens on the user.
Sparser, Better, Faster, Stronger: Sparsity Detection for Efficient Automatic Differentiation
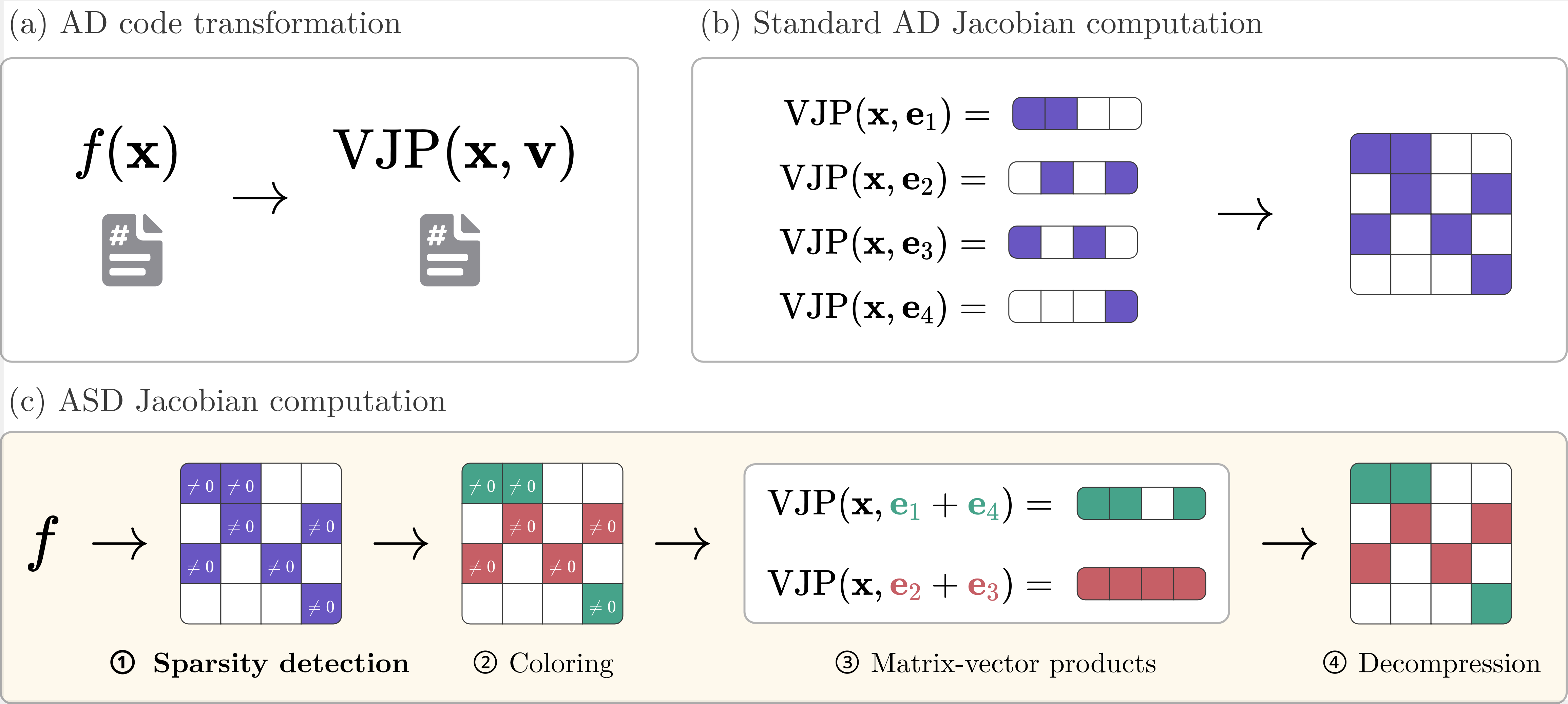
From implicit differentiation to probabilistic modeling, Jacobian and Hessian matrices have many potential use cases in Machine Learning (ML), but they are viewed as computationally prohibitive. Fortunately, these matrices often exhibit sparsity, which can be leveraged to speed up the process of Automatic Differentiation (AD). This paper presents advances in sparsity detection, previously the performance bottleneck of Automatic Sparse Differentiation (ASD). Our implementation of sparsity detection is based on operator overloading, able to detect both local and global sparsity patterns, and supports flexible index set representations. It is fully automatic and requires no modification of user code, making it compatible with existing ML codebases. Most importantly, it is highly performant, unlocking Jacobians and Hessians at scales where they were considered too expensive to compute. On real-world problems from scientific ML, graph neural networks and optimization, we show significant speed-ups of up to three orders of magnitude. Notably, using our sparsity detection system, ASD outperforms standard AD for one-off computations, without amortization of either sparsity detection or matrix coloring.
An Illustrated Guide to Automatic Sparse Differentiation
A. Hill, G. Dalle, A. Montoison
In numerous applications of machine learning, Hessians and Jacobians exhibit sparsity, a property that can be leveraged to vastly accelerate their computation. While the usage of automatic differentiation in machine learning is ubiquitous, automatic sparse differentiation (ASD) remains largely unknown. This post introduces ASD, explaining its key components and their roles in the computation of both sparse Jacobians and Hessians. We conclude with a practical demonstration showcasing the performance benefits of ASD.